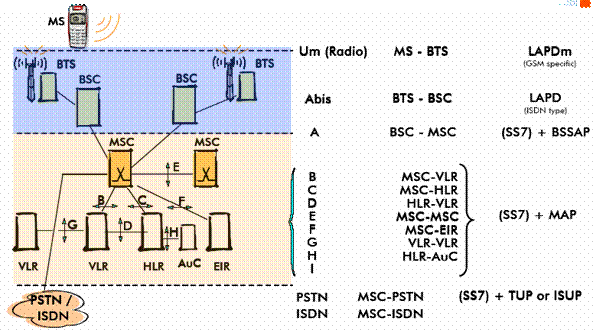
The GSM network and protocols
Mobile Services Switching Center (MSC)
The primary node in a GSM network is the MSC. It is the node, which controls calls both to MS’s and from MS’s. The primary functions of an MSC include the following:
Switching and call routing
MSC interact with other nodes to successfully establish a call. During a call it involves in handovers from one BSC to another and inter MSC handover.
Charging
MSC contains functions for charging mobile calls and information about the particular charge rates to apply to a call at any given time or for a given destination. During a call it records this information (Call Data Record-CDR) and sends it to the billing center.
Service provisioning
Supplementary services are provided and managed by a MSC. In addition, the SMS service is handled by MSC’s
Communication with HLR & VLR
MSC is communicating with HLR & VLR when call setup and release and get subscription information.
Communication with other MSCs
MSC’s communicate with each other during call setup or handovers between cells belonging to different MSC’s.
Control of the connected BSCs
An MSC may communicate with its BSC’s during; for example, call set-up and handovers between two BSC’s.
Visitor Location Register (VLR)
The role of a VLR in a GSM network is to act as a temporary storage location for subscription information for MSs which are within a particular MSC service area. Thus, there is one VLR for each MSC service area. This means that the MSC does not have to contact the HLR every time the subscriber uses a service or changes its status.
VLR contains following data.
- Identity numbers for the subscriber
- Supplementary service information (e.g. whether the subscriber has call forwarding on busy activated or not)
- Activity of MS (e.g. idle)
- Current LA of MS
Home Location Register
The HLR is a centralized network database that stores and manages all mobile subscriptions belonging to a specific operator. It acts as a permanent store for a person's subscription information until that subscription is cancelled. The information stored includes:
- Subscriber identity (i.e. IMSI, MSISDN)
- Subscriber supplementary services
- Subscriber location information (i.e. MSC service area)
- Subscriber authentication information
Authentication Center (AUC)
The primary function of an AUC is to provide information, which is then used by an MSC/VLR to perform subscriber authentication and to, establish ciphering procedures on the radio link between the network and MS’s. The information provided is called a triplet and consists of:
- A non predictable Random number (RAND)
- A Signed Response (SRES)
- A ciphering Key (Kc)
Equipment Identity Register
The equipment identification procedure uses the identity of the equipment itself (IMEI) to ensure that the MS terminal equipment is valid.
No comments:
Post a Comment